The Best Nootropics for Memory: What the Research Shows
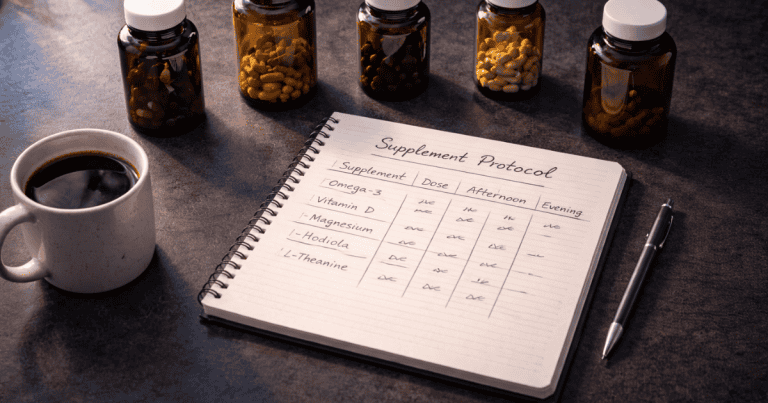
Most memory supplements are marketing claims. A small number have genuine clinical evidence. The evidence-based memory nootropic stack — Bacopa, Phosphatidylserine, Alpha-GPC, Lion’s Mane, and Magnesium L-Threonate — with mechanisms, doses, timelines, and how each compound addresses a different stage of memory formation.